The Ultimate Guide to OTT Technology for Professional Broadcasters in 2025
The influence of traditional media is dwindling. Viewers want more control and options over what they watch. Over-the-top (OTT) content delivery is the alternative taking the world by storm. Hence video streaming via OTT content providers such as Netflix, Hulu, and YouTube TV are more popular than ever.
In this ultimate guide, we cover what OTT platforms and technology are. We discuss how it works and how it’s changing the media industry. Furthermore, we discuss why you should use OTT and provide examples of successful businesses built on an OTT platform. To conclude, we compare IPTV and OTT.
Table of Contents
- What is OTT Technology?
- Why Use OTT?
- How is OTT Delivered?
- How Does OTT Technology Work?
- How OTT Technology is Changing the Media Industry
- IPTV vs. OTT
- OTT vs. Streaming
- Core Components of OTT Technology
- Detailed Workflow of How OTT Technology Works
- OTT Protocols and Streaming Technologies
- Role of OTT APIs
- Challenges in OTT Delivery and Technological Solutions
- Comparison of OTT vs. Other Video Technologies
- OTT Technology Trends and Future Developments
- How to Implement OTT Technology for Your Business
- OTT Monetization Models
- FAQs
- Conclusion
What is OTT Technology?
What is OTT?
OTT (Over-the-Top) is a method of delivering media content directly to viewers over the internet, bypassing traditional distribution methods like satellite or cable television. When providers stream with OTT technology, users can enjoy on-demand content or live broadcasts on any internet-connected device, including smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, and computers.
What is OTT Technology?
OTT technology encompasses the tools, software, and infrastructure required to deliver content online. This includes video hosting platforms, content delivery networks (CDNs), video encoding tools, and interactive streaming features that ensure seamless delivery and a high-quality viewing experience.
What is OTT Broadcasting?
OTT broadcasting refers to the process of distributing video, audio, or other media content via the internet instead of traditional broadcast methods. It empowers content creators and broadcasters to reach global audiences without relying on satellite or cable providers. OTT broadcasting makes it easy for viewers to access content on their preferred devices, anytime and anywhere.
What is an OTT Video?
OTT video specifically refers to video content streamed over the internet, bypassing traditional cable or satellite TV systems. Examples include movies, TV shows, webinars, and live events accessed through platforms like Netflix, Hulu, or YouTube.
How Does OTT Work?
OTT services bypass traditional media distribution systems by delivering content “over the top” of them via the internet. These services are monetized through various business models, including paid subscriptions (SVOD), ad-supported streaming (AVOD), transactional purchases (TVOD), or hybrid models combining subscriptions and ads. This flexibility makes OTT a powerful tool for content creators, broadcasters, and businesses alike.
Bottomline: OTT is all about going around or “over the top” of traditional media distribution channels and accessing content through the internet. OTT services are often monetized through paid subscriptions, but they can also use advertising or in-app purchases to support their broadcasting efforts.
Why Use OTT?
Wondering why as a broadcaster, you should jump onto the OTT train? The main reason is that people love OTT content. You can look at one of the biggest OTT providers, Netflix, which now has 282.7 million subscribers as of Q3, 2024.
OTT isn’t just about huge content providers. Many sports organizations, for example, now offer league passes so fans can access games and content for their favorite teams no matter where they live.
Examples of OTT sports content include big names like ESPN+ and more league-specific content such as the NBA League Pass, Premier League Pass, F1TV, and DAZN. Many college sports organizations also have their own OTT content.
People love OTT content because it is easy to access and can be targeted based on one’s viewing preferences. Broadcasters should use OTT strategies for over-the-top because it allows access to a larger audience, as there are fewer barriers to accessing OTT content than traditional TV content.
How is OTT Delivered?
OTT platforms use an internet-based delivery system. That means that all someone needs to access the content is an internet connection and a compatible device. Here are some of the most common devices people can use to access OTT platforms:
- Mobile devices: You can use either a smartphone or tablet to download OTT apps from a digital storefront, such as Google Play or Apple App Store.
- Personal computer: With a computer, you can access OTT content through a web browser or desktop-based apps.
- Digital media players: Third-party devices such as Chromecast, Apple TV, and even video game consoles can download OTT apps and access content.
- Smart TVs: Smart TVs now come with numerous pre-installed OTT apps and the ability to download additional OTT apps.
Essentially, if you have an internet connection and a device that can access the internet, you should be able to access OTT content.
How Does OTT Technology Work?
While accessing video via OTT is typically more convenient for viewers, what goes on behind the scenes of OTT streaming is a bit more complex than traditional broadcasting.
Here is how OTT technology looks in action:
- Broadcasters upload video content to an OTT video hosting platform
- The video host transmits the data to remote servers via a content delivery network (CDN)
- Viewers select the content they want to stream on the user-facing video gallery
- The video player on the device pulls the video content from the CDN’s server with the internet
With that process in mind, let’s briefly break down the technologies involved.
With that process in mind, let’s briefly break down the technologies involved. This will help you understand precisely how OTT technology works and what is meant when someone says OTT technology.
OTT Platform Technology
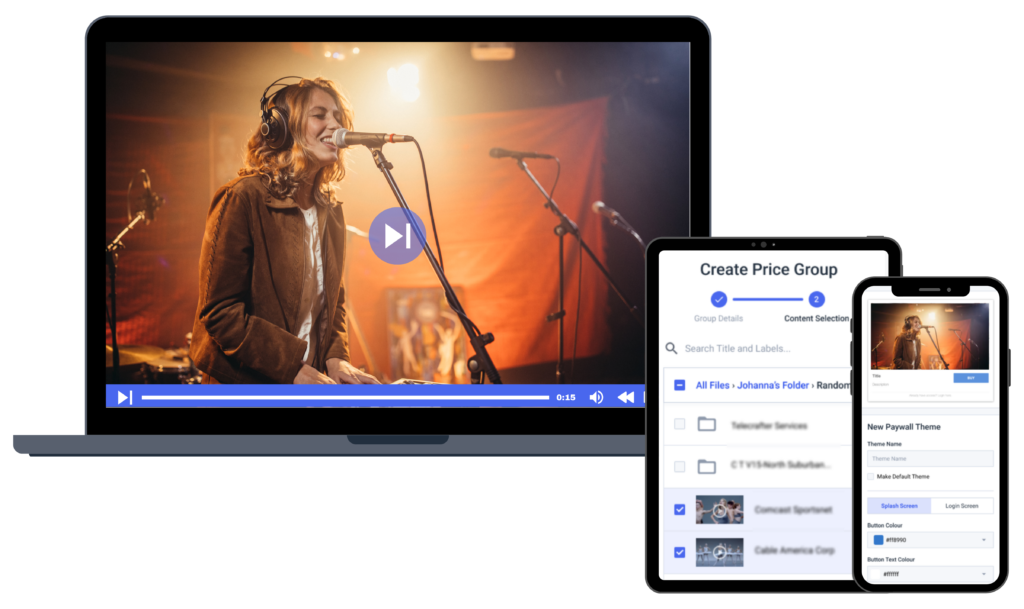
First and foremost, OTT streaming requires a professional-grade video hosting platform with OTT capabilities. OTT platform technology typically comes in downloadable software or an in-browser streaming platform.
Some OTT platform technology is open source. However, the most popular options include a graphical user interface that allows broadcasters with any level of experience to navigate OTT broadcasting easily. With the right OTT platform technology, this highly technical process becomes accessible to those with limited to no technological know-how.
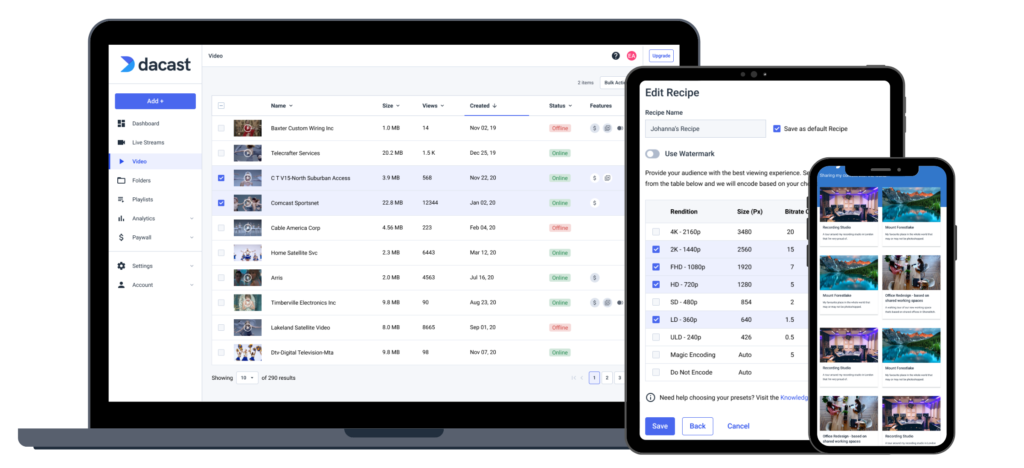
Video hosting platforms come with various tools for hosting, storing, and managing video content at different price points. Some hosting features valuable for creating your own platform include OTT model monetization, gold-standard security, HTML5 video players, white-label capabilities, brand customization, and API access.
Some of the most innovative OTT platform technology is available via Dacast, Vimeo OTT, and Brightcove. We recommend looking at our comparison of the 10 Best OTT video hosting providers for more information on this specific piece of OTT technology to find the platform that works best for you.
Content Delivery Network
OTT media distribution is made possible by content delivery networks.
A content delivery network (CDN) is exactly what it sounds like a network of servers that delivers content. Most online video platforms partner with professional CDNs, so this isn’t typically the main concern for broadcasters. To release content over an OTT, you need a content delivery network to move that content to your end viewers.
You’ll want to ensure that your chosen video hosting platform uses a CDN with servers stationed around the globe. This will help maintain the quality of your stream for viewers in every corner of the globe. It will also help avoid lagging and buffering.
However, if you are self-hosting, you must choose a CDN of your own. Due to complicated CDN pricing structures, this can get expensive and confusing, so choosing a video hosting platform with a built-in CDN is the way to go. A built-in CDN makes it easier to engage in OTT video distribution.
Internet Connection
A strong internet connection is another important piece of the OTT technology puzzle. Broadcasters need a reliable internet connection to send out their video signal, and viewers need fast internet to access content on your OTT platform, as well.
The ideal upload speed for OTT streaming is 672 kbps to 61.5 Mbps. For high-quality streaming, your internet speed should be about double your intended bandwidth usage.
You can check your internet speed by searching for an “internet speed test” on Google. Be sure to pay attention not to your download speed, which is what most people focus on when looking at internet speed, but to your upload speed.
Regarding appropriate download speeds for viewing OTT content, there is a bit of variety in what is considered “good.” The recommended speeds depend on the quality of the video the viewer is trying to access.
The recommended download speeds are broken down as follows:
- 25 Mbps: sufficient for streaming 1080p HD video
- 10 Mbps: sufficient for 720p video
- 5 Mbps: sufficient for 480p video
Most viewers access OTT content with their in-home WiFi, and viewers on the go will tune in with their cellular data. In-home WiFi is typically more reliable, but cellular data can work, as well. With different download speeds based on in-home and on-the-go access, you will want to look into adaptive bitrate or multi-bitrate streaming for the best experience for your viewers.
App with Embedded Video Players
To make your OTT video content easily accessible to viewers, you need to build a platform that displays your library of video content and can embed your video player to stream your content online. Many OTT platforms offer desktop, Smart TV, and mobile versions to maximize compatibility and accessibility.
Make sure that the professional video hosting platform you’re using offers API access and mobile SDKs to create a platform that perfectly suits your audience.
Internet-Enabled Device
This may seem like a no-brainer, but an internet-enabled device is a non-negotiable for OTT streaming. Viewers need to have a device that they can use to access video players on your OTT platform.
We will dive a little further into this shortly, but OTT video can be accessed on computers, Smart TVs, and more.
How OTT Technology is Changing the Media Industry

OTT technology has played a massive role in the media industry’s evolution. It is leading viewers worldwide to “cut the cord” on cable. As of the third quarter of 2024, 6.6 percent of U.S. households cut the cord. The number of pay TV subscriptions is likely to further drop in the near future as more and more people opt for streaming services.
Access to OTT technology changes the traditional television-watching experience in a few different ways. For starters, viewers can access their favorite shows and films from just about any device with internet capabilities.
The ability to sign in to your OTT streaming platform account on different devices allows you to access your subscriptions from anywhere in your house without worrying about special wiring or hookups.
You can also access the subscriptions or videos you’ve purchased if you’re on vacation by signing in on your smartphone, laptop, or tablet. The flexibility that comes with cutting the cord is so convenient, and it allows viewers to get the most out of their subscriptions.
OTT streaming brings exciting developments for broadcast sports fans in particular. With traditional television, some games are only available in certain regions. Other areas are total blackout zones due to their proximity to multiple major cities. With OTT, you can watch your favorite sports team from anywhere in the world.
A major OTT trend that has grown alongside the industry is binge-watching. Netflix and other platforms release entire series of seasons at a time, as opposed to the airing of weekly episodes that traditional TV uses. This has inspired people to binge-watch shows out of excitement or fear of the plot being spoiled by family, friends, or other users on social media.
OTT technology has influenced the way that we consume video content.
Examples of OTT Devices
OTT technology has changed how video content is accessed. As we mentioned, there are quite a few OTT devices, which is convenient because viewers aren’t restricted to their television set if they want to watch a film or show.
Here are a few specific examples of OTT devices:
- Smartphones: iPhones and Androids
- Tablets: iPad, Amazon Fire, Microsoft Surface, Galaxy Tab A
- Smart TVs: Roku TV, Apple TV, Amazon Firestick, Chromecast
- Gaming Consoles: XBOX, Play Stations
Although most OTT platform providers are designed and marketed as a replacement for traditional television, over half of OTT viewers tune in from their mobile devices. OTT technology works on any type of device when paired with an HTML5 video player. Mobile viewing continues to increase and replace traditional television viewing, with OTT video helping to fuel this trend.
Examples of Businesses Built Upon OTT Technology

Pretty much all of the major streaming-as-a-service platforms that consumers know and love are powered by OTT technology. Some examples are Hulu, Disney+, Prime Video, and Netflix.
Each of these businesses monetizes its content in slightly different ways.
Netflix, which started as a video rental company, is probably one of the most notable businesses that have evolved to accommodate the shift towards OTT broadcasting. Netflix adapted its model from DVD rentals to online video streaming throughout the past decade. They stayed on the cutting edge of OTT technology to launch their streaming service as soon as the internet became more accessible and bandwidth costs were affordable.
Today, Netflix generates over $37.587 billion in revenue (as of the end of year 2024) from its subscription-based OTT streaming platform.
Prime Video uses a mix of subscriptions and pay-per-view monetization. Prime Video offers access to a library of films and television series to those with an Amazon Prime membership. Still, a large chunk of their content is only available at an added cost. Viewers can rent movies and shows to watch right on the platform.
Hulu uses a combination of advertisements and subscriptions to monetize its platform. Users can pay extra to upgrade to ad-free streaming. Hulu also offers upgrades for access to live-streamed programs and channels with linear streaming.
Disney+ is available via subscription on its own, but the platform has strategically partnered with different platforms, including Hulu, to reach a larger audience. Another one of their partners is ESPN+, which is popular among different demographics. However, these bundles are priced right, making them attractive to families with members with other interests.
Video OTT can be packaged and priced in many ways, as evidenced by the above examples.
IPTV vs. OTT
While we’re on the topic of OTT technology, let’s clear up a common confusion in online video streaming. Many people wonder what the difference is between IPTV and OTT. The two are very similar and seem identical on the surface, so this is a valid question.
IPTV is short for “Internet Protocol Television,” and it is another alternative to traditional television that uses the internet to stream. The main difference between IPTV and OTT streaming is that IPTV uses a closed server and OTT does not.
IPTV is also typically very similar to traditional television because it primarily uses linear broadcasting. It is generally packaged as a channel rather than access to an extensive library of content. On-demand streaming is possible with IPTV, but it is not nearly as popular as OTT.
It is very popular for large enterprises and organizations to use IPTV for internal video hosting and delivery, whereas streaming services like Netflix and Hulu rely on OTT.
OTT vs. Streaming
OTT technologies and traditional streaming services both deliver content online, but there are key differences. OTT (over-the-top) platforms offer direct access to video content over the internet, bypassing cable or satellite providers. Examples of OTT in media include Netflix, Hulu, and Disney+.
You may ask, How does OTT work? It works by using the internet to stream content directly to users on any device, such as smart TVs, smartphones, or tablets. How OTT platform works is through content delivery via apps or websites, without needing a broadcast service.
When comparing OTT vs streaming, streaming is the general process of delivering audio or video in real time, while OTT platforms provide more control over the distribution and monetization of content. For a deeper understanding, refer to an OTT guide to see how this technology is transforming media consumption.
Core Components of OTT Technology
OTT video technology powers the delivery of content directly to viewers over the internet. The OTT platform architecture consists of several critical components. First, video encoding and transcoding are essential for compressing videos while maintaining quality. This ensures smooth playback across various devices. Streaming protocols like HLS and MPEG-DASH are used to deliver content over OTT networks, allowing for adaptive streaming and high-quality viewing experiences.
A video CMS (Content Management System) helps manage, organize, and distribute content efficiently. Content monetization is another major element, with methods like subscriptions, ads, and pay-per-view enabling revenue generation for OTT streaming services. OTT distribution ensures that content reaches a wide audience, making it accessible globally. For further insights on OTT in media and answering questions like what is the difference between OTT and IPTV, explore a detailed OTT guide for a larger overview.
Detailed Workflow of How OTT Technology Works
To understand how OTT platforms operate, let’s break down the process from content creation to viewer delivery:
- Content Ingestion: The first step involves capturing or uploading video content to the OTT platform. This content can be live (e.g., a live sports event) or pre-recorded (e.g., a movie or TV series). The ingestion process ensures the content is properly received and organized for further processing.
- Cloud Transcoding: After ingestion, the video undergoes transcoding in the cloud. This step converts the video into multiple formats, bitrates, and resolutions to ensure compatibility with a wide range of devices, including smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, and desktops. Adaptive bitrate streaming is often used to dynamically adjust video quality based on the viewer’s internet speed.
- Content Delivery via CDNs (Content Delivery Networks): Transcoded content is then distributed through CDNs. These networks consist of geographically distributed servers that store and deliver the content from locations closer to viewers. This reduces latency, prevents buffering, and ensures a smooth streaming experience.
- Viewer Delivery: The final step involves delivering the processed content to the viewer’s device. Users can access the content on-demand or as part of a live stream through OTT apps or web platforms, enjoying seamless playback anytime, anywhere.
OTT Protocols and Streaming Technologies
OTT technology drives the delivery of video content directly to viewers over the internet, bypassing traditional distribution channels like cable and satellite systems. At the core of this technology are advanced streaming protocols and tools designed to ensure high-quality, reliable, and secure content delivery under diverse network conditions.
Key Streaming Protocols for OTT Delivery
- HLS (HTTP Live Streaming):
HLS is the industry standard for adaptive streaming and is widely used for OTT content delivery. Developed by Apple, HLS or HTTP Live Streaming is praised for its ability to deliver high-quality video content to a broad range of devices, including smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, and computers. It segments video into smaller chunks, enabling adaptive bitrate streaming (ABR) and ensuring smooth playback even with fluctuating internet speeds. - RTMP (Real-Time Messaging Protocol):
RTMP is a low-latency protocol that is especially popular for live broadcasting. While it has largely been replaced by HLS and other modern protocols for final delivery, RTMP-enabled solutions remain a crucial part of the streaming workflow for transmitting video from an encoder to a server or CDN (Content Delivery Network). Its real-time capabilities make it ideal for live events, webinars, and interactive streaming. - MPEG-DASH (Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP):
Similar to HLS, MPEG-DASH is an adaptive bitrate streaming protocol that works across multiple devices and browsers. Unlike HLS, which primarily supports Apple devices, MPEG-DASH is codec-agnostic and universally compatible, offering flexibility for OTT platforms targeting global audiences.
Adaptive Bitrate Streaming (ABR)
Adaptive Bitrate Streaming is a foundational technology for OTT platforms. By dynamically adjusting video quality in real-time based on the viewer’s internet connection, ABR ensures uninterrupted playback with minimal buffering. This technology divides video files into segments of different quality levels, allowing the streaming client to switch between them as needed. ABR is particularly valuable for maintaining viewer satisfaction in regions with inconsistent or lower bandwidth.
Digital Rights Management (DRM)
Security is a critical concern for OTT platforms, particularly when handling premium or copyrighted content. Digital Rights Management (DRM) systems play a vital role in protecting OTT video content from unauthorized access and piracy. DRM technologies like Widevine, PlayReady, and FairPlay encrypt video streams, ensuring that only authorized users can access the content. This safeguards intellectual property and supports monetization efforts for subscription-based or pay-per-view services.
Content Delivery and Latency Reduction
Modern OTT platforms rely heavily on Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) to distribute video efficiently and reduce latency. CDNs cache video content on servers located closer to end users, ensuring fast load times and reducing buffering. For low-latency streaming—crucial for live sports, gaming, and interactive events—technologies like WebRTC and Low Latency HLS (LL-HLS) are becoming increasingly popular.
Emerging OTT Technologies
The evolution of OTT streaming includes new technologies such as AI-driven video encoding optimization, real-time analytics, and immersive streaming formats like VR and AR. These advancements enhance the viewer experience and provide platforms with actionable insights to improve content delivery and audience engagement.
Role of OTT APIs
APIs play a crucial role in OTT media services. They allow for seamless integration of OTT content delivery into various platforms. These OTT APIs enable businesses to customize their digital OTT solution by embedding them into websites, applications, or even what is an OTT device, such as smart TVs and streaming devices.
In the OTT industry, APIs are essential for creating a smooth user experience, enabling viewers to access streaming OTT content easily across different devices. With APIs, businesses can tailor their OTT media services to meet specific needs, from managing subscriptions to delivering personalized recommendations. As a result, APIs help improve efficiency and enhance the overall user experience, ensuring that OTT content delivery is flexible and scalable across multiple platforms.
Challenges in OTT Delivery and Technological Solutions
OTT video services face several challenges in delivering high-quality streaming experiences. Latency is a common issue, where delays between real-time events and the stream frustrate viewers, especially during live broadcasts. Another challenge is scalability during live events, as a sudden surge in viewers can overload servers, leading to buffering or outages. Managing various devices is also complex, as viewers use different smartphones, tablets, and smart TVs, each with unique requirements.
Modern OTT technology addresses these problems with advanced solutions. Edge computing reduces latency by processing data closer to users, speeding up delivery. Adaptive bitrate streaming improves scalability and user experience by adjusting video quality based on the viewer’s network conditions and device capabilities, ensuring smooth streaming regardless of bandwidth fluctuations or device specifications. These innovations significantly enhance the reliability and flexibility of OTT video services.
Comparison of OTT vs. Other Video Technologies
Over-the-top technology has transformed the way we access video and audio content. Unlike traditional broadcasting, which relies on cable or satellite networks, OTT delivers content directly over the internet. This allows viewers to watch shows, movies and videos on demand, making it a popular choice for consumers seeking flexibility.
In contrast, IPTV also streams video content over the internet but usually requires a subscription through a service provider. This can limit access compared to OTT, which can be accessed through various devices without a subscription
Traditional broadcasting, such as terrestrial or satellite TV, offers limited interactivity and content choice. Viewers are often tied to fixed schedules. By contrast, OTT platforms allow users to watch content anytime, anywhere.
Hybrid models combine elements of both OTT and IPTV, providing a mix of live streaming and on-demand content. While these technologies offer different benefits, OTT stands out for its convenience, user control, and extensive content library, making it a preferred choice for many viewers today.
OTT Technology Trends and Future Developments
The OTT streaming industry is constantly growing and evolving, driven by several key trends. Before we wrap things up, let’s take a look at a few interesting trends in this industry:
- The AI for video streaming trend is driven by the need to enhance user engagement and satisfaction by offering tailored suggestions based on viewing habits, preferences, and behavioral patterns.
- It is expected that OTT video hosting platforms in 2025 will continue to rise as more viewers seek specialized content.
- As viewers demand more options for accessing content, hybrid streaming models that blend different content monetization methods are set to gain momentum.
- OTT Platform providers will invest in fast load times, intuitive interfaces, and seamless content discovery to improve user satisfaction.
- The growing demand for high-definition video, especially for live sports, movies, and documentaries, is driving the rise of 8K and 4K streaming in 2025, with OTT platforms enhancing their networks to support UHD streaming.
- Smart TVs, along with gaming consoles and streaming devices, are driving the rise of Connected TV (CTV) by enabling viewers to enjoy immersive OTT streaming on large home screens.
- Cloud technology is transforming OTT streaming by enabling cost-effective scalability, seamless cross-device access, and reliable integration of live and on-demand content.
For more information on these and other 2025 OTT trends, please check out our dedicated guide.
How to Implement OTT Technology for Your Business: A Guide
Implementing OTT technology can transform your business by allowing you to deliver video content directly to your audience, bypassing traditional media channels. Here’s a step-by-step guide to successfully integrate OTT into your operations:
1. Define Your Business Goals and Audience
Start by identifying what you aim to achieve with OTT technology. Are you looking to monetize content through subscriptions (SVOD), ads (AVOD), or pay-per-view (TVOD)? Or are you focusing on brand engagement or audience retention? Additionally, understand your target audience’s preferences, device usage, and content consumption habits to tailor your OTT service effectively.
2. Choose the Right OTT Platform
Research and select an OTT platform that aligns with your business goals. Look for features such as:
- Video Hosting and Management: Easy upload, storage, and organization of content.
- Adaptive Streaming Support: Ensures seamless playback across devices.
- Monetization Options: Includes support for subscriptions, ads, or pay-per-view models.
- Analytics Tools: Provides insights into viewer behavior and content performance.
- Scalability: Accommodates audience growth and increased traffic.
3. Plan and Secure Your Content
Decide on the type of content you want to offer, such as live streams, on-demand videos, or both. Make sure you have the necessary rights to distribute all content. Invest in tools for content encoding and transcoding to ensure compatibility across devices.
4. Integrate a Reliable Content Delivery Network (CDN)
Partner with a reputable CDN to ensure your content is delivered quickly and efficiently to viewers across the globe. A good CDN minimizes latency, enhances streaming quality, and can scale with your audience. Consider CDNs that support low-latency streaming for live events or interactive content.
5. Implement Branding and User Experience (UX)
Customize your OTT platform to reflect your brand identity. This includes:
- Branded video players with logos and color schemes.
- User-friendly navigation and search functionality.
- Multi-language support for global audiences.
- Accessibility features, such as closed captions and audio descriptions.
6. Ensure Content Security and Compliance
Protect your content with Digital Rights Management (DRM) technologies, encryption protocols, and secure payment gateways to prevent piracy and unauthorized access. Ensure compliance with privacy regulations such as GDPR or CCPA if applicable.
7. Test Your Setup Thoroughly
Before launching, conduct extensive testing to identify and resolve any issues. Test for:
- Video Quality: Ensure videos load quickly and maintain high quality across devices.
- Adaptive Bitrate Streaming: Verify seamless playback under varying network conditions.
- User Experience: Evaluate navigation, responsiveness, and overall platform usability.
8. Launch and Promote Your OTT Service
Once your platform is ready, launch it with a comprehensive marketing strategy to attract viewers. Use channels like:
- Social media campaigns.
- Email marketing.
- Partnerships with influencers or content creators.
- Paid ads to drive traffic and build awareness.
9. Monitor Performance and Optimize
Post-launch, track key performance indicators (KPIs) like viewer engagement, subscription rates, and content popularity. Use analytics tools to gather insights and make data-driven improvements to your platform.
OTT Monetization Models
OTT content providers have various monetization models to generate revenue while delivering engaging video experiences.
1. Subscription Video on Demand (SVOD): This model allows users to pay a recurring fee for access to a library of content. Popular platforms like Netflix and Disney+ use SVOD to ensure a steady income.
2. Advertising Video on Demand (AVOD): In this model, content is free for viewers, but ads are shown during the programming. Platforms like YouTube utilize AVOD, making it accessible to a wide audience while generating revenue from advertisers.
3. Transactional Video on Demand (TVOD): Here, users pay for individual pieces of content, such as movies or episodes. This model is common on platforms like iTunes, where customers can rent or buy specific titles.
4. Hybrid Models: Combining elements of SVOD, AVOD, and TVOD, hybrid models offer flexibility for content creators and viewers. This approach allows providers to maximize revenue while catering to diverse audience preferences.
FAQs
1. What is OTT?
OTT stands for “over-the-top.” This refers to content delivered directly to viewers via the internet, rather than by traditional cable or satellite services.
2. How does OTT work?
OTT works by streaming video content through apps or websites on devices like smart TVs, smartphones, or tablets. This allows users to access shows and movies at any time of day.
3. What’s the difference between OTT and streaming?
While streaming refers to the delivery of content over the internet, OTT refers to bypassing traditional distribution channels.
4. Do I need a subscription for OTT services?
No, not always. Some OTT services are subscription-based (SVOD), while others are ad-supported (AVOD) or offer pay-per-view (TVOD) options.
5. What types of content are available on OTT platforms?
OTT platforms offer a wide variety of content. This includes movies, TV shows, documentaries, and live sports.
6. Is OTT content available worldwide?
Availability can vary by region, as some platforms may restrict access based on licensing agreements.
Conclusion
With OTT, broadcasters can create profitable streaming services and deliver video on demand that viewers crave. Delivering high-quality video content partnered with an HTML5 streaming video solution will bolster your professional presence.
Looking to build a professional, top OTT platform of your own? Look no further than Dacast. Dacast’s professional-grade OTT platform technology has the tools you need to host and deliver incredible OTT content. Using HTML5 video player and partnered with top-tier CDNs, Dacast provides the best possible OTT broadcasting experience.
You can try Dacast completely free for a full 14 days.
Feel free to join our LinkedIn group for regular tips on live streaming and exclusive offers.
 Stream
Stream Connect
Connect Manage
Manage Measure
Measure Events
Events Business
Business Organizations
Organizations Entertainment and Media
Entertainment and Media API
API Tools
Tools Learning Center
Learning Center Support
Support Support Articles
Support Articles