The Definitive Guide to Video Streaming Technology in 2025
Video streaming technology has revolutionized the way businesses and individuals share and consume content. Whether it’s live streaming a product launch, hosting virtual events, delivering training sessions, or providing entertainment through on-demand video services, streaming technology is now an essential part of digital communication and commerce.
Over the past decade, advancements in streaming protocols, AI-driven enhancements, and content delivery networks (CDNs) have significantly improved the quality, accessibility, and security of video streaming. The growing adoption of 5G, edge computing, and immersive experiences like virtual reality (VR) has further accelerated the evolution of streaming, making ultra-low latency, high-resolution video more accessible than ever.
In this guide, we’ll explore the fundamental components of video streaming technology, the latest innovations shaping the industry in 2025, and how businesses can leverage these advancements to optimize engagement, monetization, and security. Whether you’re a content creator, media company, or enterprise looking to integrate video streaming into your operations, this guide provides a comprehensive roadmap to navigating the future of digital video distribution.
Table of Contents
- What is Video Streaming Technology?
- How Does Streaming Video Technology Work?
- Video Streaming Basics
- Video Streaming Technology Stack
- Different Types of Video Streaming Technology
- Streaming Protocols
- Codecs
- Video Players
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
- AI-Driven and Latest Technologies in 2025
- Business Applications of Streaming Technology
- Emerging Trends in Video Streaming for Business
- How Businesses Leverage Video Streaming Technology for Growth
- Notable Video Streaming Equipment and Tools
- Emerging Video Streaming Technology for 2025
- Deep Dive into Low-Latency and Interactive Streaming
- Security and Compliance Considerations in 2025
- FAQ
- Conclusion
What is Video Streaming Technology?
Video streaming technology enables real-time delivery of video and audio content over the internet without requiring full file downloads. It works by breaking down video files into small data packets that are sent sequentially to viewer devices, allowing immediate playback. This eliminates the need for users to wait for complete downloads before watching content.
Businesses leverage streaming technology for various applications, including webinars, virtual events, e-commerce, corporate communications, and entertainment platforms. Popular video streaming services like Netflix and YouTube use this technology to provide on-demand content, while live streaming capabilities enable real-time broadcasts of events. By utilizing advanced streaming technology, businesses can offer seamless, high-quality viewing experiences to global audiences.
How Does Streaming Video Technology Work?
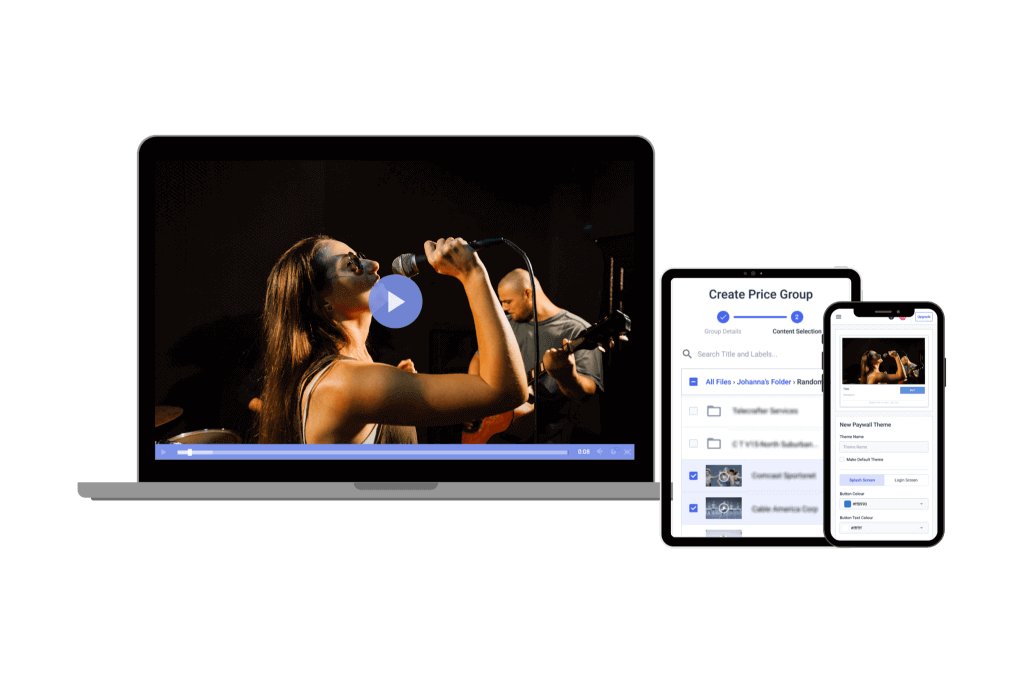
Online video streaming is a science that is still being optimized. However, the technology that is currently available is very powerful and makes it possible to stream video live.
Viewers from around the world can attend a single event without leaving the comfort of their homes. This has revolutionized the way that we learn and carry out business. It has even changed the way that we consume media and engage in activities for leisure. This is possible due to video streaming technology.
There is so much that goes on behind the scenes to bring viewers high-quality video content as it plays out in real time. Before we dive into the nitty-gritty of these technologies, it is important to understand the path that a video takes from the time it is recorded on a camera until it reaches viewers’ screens.
The online video streaming setup typically looks like this:
- The camera captures RAW video
- Video is sent to the encoder via capture card or another hookup
- The encoder converts RAW video to a digital file
- Video is ingested into the online video platform
- The video is distributed from the online video platform to the video player via a content delivery network
- The video player displays the stream on the viewer’s internet-enabled device
This setup may vary, depending on the specific tools you’re using. Those are the basics of how online video streaming works.
Video Streaming Basics
Video streaming has changed the game in terms of how content is consumed and distributed. It presents immense opportunities for broadcasters and businesses alike. At its core, video streaming technology involves delivering video and audio content over the internet in real time. This allows viewers to watch videos without the need to download files seamlessly.
Key to this is the video streaming infrastructure. This includes servers, CDNs, and streaming protocols. The infrastructure ensures the content is efficiently distributed and streamed to users across various devices. Then, encoding compresses the video into manageable sizes, while media servers store and deliver content. Embedded in websites and apps, players decode and play the streamed media.
Streaming media technology supports different types of streaming content such as live broadcasts, on-demand videos, and interactive streams. Furthermore, broadcast video technology integrates traditional TV and online platforms. This integration broadens reach and engagement. With continuous advancements in audio and video streaming technology, high-quality, low-latency streaming is more accessible than ever.
The latest streaming technology trends focus on enhanced viewer experience. This includes 4K resolution, adaptive bitrate streaming, and immersive VR/AR content. Understanding the basics of video streaming technology equips businesses and broadcasters with the tools they need to leverage these innovations. As a result, they ensure their content remains competitive in the ever-evolving landscape of online video streaming technologies.
Video Streaming Technology Stack
The video streaming technology stack is essential for delivering high-quality online video technology. This stack consists of several major components including encoding, streaming servers, content delivery networks (CDNs), and playback devices.
What is streaming technology and how does video streaming work? To understand what streaming technology entails begins with encoding. Encoding compresses the video into manageable sizes without sacrificing quality. Next, streaming server technology hosts and delivers the video to users. Then, CDNs distribute this content across global networks, reducing latency and buffering times.
How video streaming works on the web involves these components working together seamlessly. Let’s say a user requests a video. The encoded video file gets sent from the streaming server through the CDN to the user’s device. It’s here that a media player decodes and plays it for the user. Streaming technology examples that facilitate this include popular platforms such as Netflix and YouTube.
By grasping the video streaming basics, businesses can use the video streaming technology stack effectively to provide the best viewing experiences possible and remain competitive.
Different Types of Video Streaming Technology
From reviewing the video streaming setup we mentioned above, you can see that there are a lot of moving parts. Several different types of video streaming technology come together to create a seamless streaming experience.
The four major types of streaming technology include streaming protocols, codecs, video players, and content delivery networks. Each of these key components works together to transmit video from point A to point B.
Let’s take a closer look at each of these video streaming technologies and the roles that they play in online video streaming.
Streaming Protocols
Streaming protocols are standardized methods of delivering media across the internet. They take small chunks of data to make them light enough to carry over a variety of internet connections.
Protocols are important for broadcasting because they carry the content from one point to the next in the video streaming process.
There are several video streaming protocols that are important for live streaming. Let’s take a look at a few that are most commonly used today.
1. HLS
The HTTPS Live Streaming (HLS) protocol is one of the most important protocols in video streaming technology today. This protocol was founded by Apple to work with the HTML5 video player. It is used to deliver the media from the content delivery network to the user-facing player.
HLS can also be used for ingesting media from the encoder to the online video platform, but since HLS encoders are not that popular yet, HLS delivery is typically paired with RTMP ingest.
2. RTMP
Real-Time Messaging Protocol (RTMP) is another very important protocol that broadcasters use today. This was created to deliver content to Adobe’s Flash player, but since this video player has died out, it has assumed another role in streaming.
Today, this protocol is used for RTMP ingest. That means that it transports videos from the encoder to the online video platform or directly to the content delivery network.
RTMP provides the benefit of low-latency streaming and access to affordable RTMP encoders.
3. RTSP
Real-Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) is a lesser-known protocol that is actually quite important. It is often confused with RTMP, but the two are not one and the same.
RTSP is used to carry commands from the user to the video player. For example, it tells the video player when the user is clicking Play, Pause, Fast-Forward, and other in-player commands.
RTSP is also valuable because it allows viewers to access video content before it is completely downloaded. This enhances the viewer experience because it doesn’t keep them waiting to play their desired content.
4. MPEG-DASH
MPEG-DASH is an open-source streaming standard that is structured similarly to HLS. What sets this standard apart is that it was the first to support adaptive bitrate streaming. This allows viewers to automatically access a stream in the quality that is best suited for their internet speed. That way, people with slower internet don’t experience excessive lagging and buffering.
MPEG-DASH is typically lumped in with streaming protocols, but it actually operates with the help of TCP, which is another protocol.
This standard is slowly gaining the support of related technology, so its compatibility is growing.
Streaming protocols are an essential piece of video streaming technology that allows for the smooth transportation of data over the internet.
Comparison of Major Video Streaming Protocols in 2025
In 2025, businesses have several video streaming protocols to choose from, each designed for different needs.
HLS: HLS remains the most widely used, offering broad compatibility and adaptive bitrate streaming, but it has higher latency. LL-HLS (Low-Latency HLS) improves on this by significantly reducing delay, making it ideal for interactive applications.
WebRTC: This is a top choice for ultra-low latency, enabling real-time communication without buffering. This makes it essential for live events, gaming, and video conferencing.
SRT: Preferred for high-quality, secure video transmission over unpredictable networks, ensuring stability for professional broadcasting.
MPEG-DASH: Provides an alternative to HLS with support across multiple platforms, but it lacks native support on Apple devices.
Selecting the right protocol depends on a business’s priorities, whether it is reach, latency, security, or quality.
Codecs
When you record a video on a camera, the RAW video files are made up of thousands of still frames that produce the fluid motion that we know as video. However, these files are very bulky which makes them un-streamable. In order for them to be made streamable, they need to be converted into a digital file.
In order to convert videos into a digital file, stills that are duplicates and deemed unnecessary are thrown out or compressed for transportation. A codec, which is a portmanteau for “coder-decoder,” is the technology that makes that happen. There are 2 types of codecs: audio codecs and video codecs.
Basically, a codec packs up the video files that it receives, transports them from one stop in the streaming process to the next. They keep their contents compact to make it easy for them to travel over the internet.
The tools that use codecs are called “encoders.” There are both hardware and software encoders, and we will talk more about these tools a little later on.
Encoders are a vital piece of video streaming technology that takes your RAW video files, and turns them into digital files that can be shared online.
Video Players
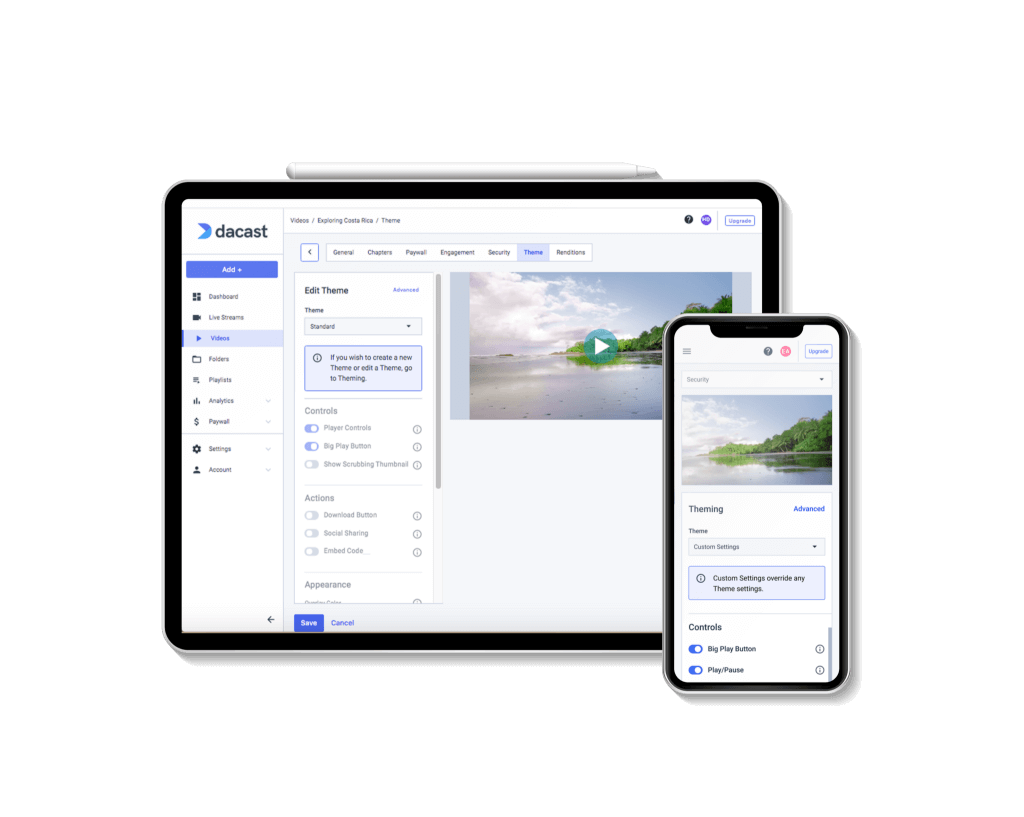
A video player is a user-facing technology that lets viewers see a video stream. In the past, Adobe’s Flash player was the standard, but since it was not compatible with mobile streaming, it has since become obsolete.
The HTML5 video player has since become the industry standard. This video player was founded by Apple to support mobile video streaming. The HTML5 video player is supported on pretty much any internet-enabled device, including smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, and gaming consoles. HTML5 is also compatible with most browsers and operating systems.
In addition to ultra-compatibility, HTML5 video players are very secure and easily customizable. Since it has so many benefits for broadcasters, HTML5 is the standard for most live-streaming platforms.
A video player is a user-facing piece of video streaming technology that allows the end-user to watch your content.
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
A content delivery network (CDN) is a series of servers that are strategically placed over a geographic region to deliver high-quality content to locations that are remote from the stream’s source.
How it works is the streaming CDN sends the content to a network of servers. Users select their desired content via video players connected to the online video platform. From there, the CDN will redirect the request from the originating site’s server to a server in the CDN that is closest to the user and deliver the cached content.
By having servers placed closer to both the origination point and the destination, content can be delivered much faster.
Many broadcasters access CDNs via partnerships formed via their selected online video platform. Dacast, for example, partners with Akamai, Limelight, and other top-tier CDNs to provide fast, high-quality streaming to viewers around the world.
Take a look at our comparison of video CDNs for video streaming to learn more about the top options on the market.
A content delivery network is an essential piece of video streaming technology that ensures you are able to get your content to your viewers smoothly around the world.
AI-Driven and Latest Technologies in 2025
AI-Powered Video Enhancement
AI-driven video streaming is revolutionizing the way content is delivered and consumed. Advanced tools like NVIDIA RTX Video Super Resolution and Topaz AI enhance video quality in real time, offering features such as upscaling lower-resolution videos, reducing noise, and improving clarity. AI also enables automatic subtitle generation and real-time video compression, optimizing content for different devices and network conditions. These innovations not only enhance user experience but also improve Video SEO by making content more accessible and discoverable.
AI-Based Content Moderation
AI plays a crucial role in moderating content on major OTT streaming services. Platforms like YouTube use machine learning to detect copyrighted material and harmful content in live streams, ensuring compliance with regulations. This automated approach reduces the need for manual moderation, making content delivery network optimization more efficient. AI-driven content filtering enhances platform safety and reliability while maintaining a seamless viewing experience.
AI-Driven Personalization and Recommendations
Streaming platforms leverage AI to analyze user behavior and preferences, enabling them to deliver personalized content recommendations. By utilizing machine learning algorithms, these platforms increase engagement and retention rates. AI-driven personalization creates immersive video experiences by curating content tailored to individual viewers, ensuring they find relevant and engaging videos more quickly. This approach benefits both users and businesses by driving higher watch times and subscription rates.
5G-Powered Streaming
5G streaming technology is transforming the industry by enabling ultra-low latency video delivery. With faster data speeds and reduced buffering, users can enjoy high-quality live streaming without interruptions. This advancement supports adaptive bitrate streaming, allowing content to be delivered smoothly even under varying network conditions. The widespread adoption of 5G enhances mobile streaming experiences and expands the reach of high-quality content.
Edge Computing and Decentralized Streaming
Edge computing in video streaming reduces latency by processing data closer to the end user. This approach enhances performance, particularly for live streaming and real-time interactions. Additionally, decentralized streaming platforms like Theta Network utilize blockchain to distribute video content more efficiently. By leveraging peer-to-peer networks, these platforms improve scalability and reduce infrastructure costs. These innovations are shaping the future of video delivery, making it more reliable and cost-effective for businesses and consumers alike.
Business Applications of Streaming Technology
Corporate Webinars and Virtual Events
Businesses increasingly rely on live streaming for internal communication, training, and large-scale virtual events. Secure video streaming solutions help companies host confidential corporate meetings and training sessions without the risk of unauthorized access. Low-latency streaming protocols ensure that interactions during live events feel natural, improving engagement during Q&A sessions and team discussions. Additionally, WebRTC streaming allows real-time collaboration, making it an essential tool for remote teams and global enterprises.
Live Shopping and Shoppable Videos
E-commerce is evolving with live streaming for business, particularly in the form of live shopping and shoppable videos. Retailers can showcase products in real time, allowing viewers to interact with hosts and make purchases instantly. This creates a dynamic and engaging shopping experience that blends entertainment with commerce. The use of the H.265 codec enhances video quality while reducing bandwidth costs, ensuring smooth playback even for large audiences. As more brands adopt interactive video strategies, live shopping is becoming a powerful tool for increasing sales and customer engagement.
AI-Powered Ad Insertion for Monetization
Video monetization strategies are more sophisticated than ever, thanks to AI-driven solutions. Dynamic ad insertion (DAI) uses artificial intelligence to place relevant ads seamlessly into live streams and on-demand videos. This ensures a personalized viewing experience while maximizing ad revenue. Secure video streaming solutions also help prevent unauthorized access to premium content, ensuring that businesses can safely monetize their video assets. AI-powered monetization tools allow companies to optimize ad placements based on user behavior, making advertising more effective.
Streaming in the Metaverse and VR Conferences
As virtual spaces grow, businesses are leveraging immersive streaming technology for events, training, and networking. The metaverse enables companies to create interactive experiences where attendees can engage with content in a 3D environment. Low-latency streaming protocols ensure that virtual conferences and VR events feel seamless, while WebRTC streaming supports real-time interactions between participants. These advancements open new opportunities for companies to host engaging, large-scale virtual events with global reach.
Monetization and Business Growth Strategies with Streaming
Subscription Models (SVOD) and Ad-Supported Models (AVOD)
Businesses use different monetization models to generate revenue from video streaming. Subscription-based services (SVOD), like Netflix, charge users a recurring fee for unlimited access to content. This model works well for companies that offer exclusive or premium content. On the other hand, ad-supported streaming (AVOD) allows users to watch content for free while businesses earn revenue through advertisements. Platforms like YouTube and Pluto TV successfully use AVOD by delivering targeted ads to viewers, maximizing engagement and revenue.
Hybrid Monetization Models
Many businesses combine SVOD, AVOD, and transactional video on demand (TVOD) to diversify revenue streams. Hybrid models allow users to subscribe for premium access while offering free, ad-supported content to attract a broader audience. Some platforms also use pay-per-view (TVOD) for exclusive events or new releases. This flexible approach helps businesses balance revenue and accessibility.
AI-Powered Content Discovery and Engagement
AI-driven recommendations keep users engaged by analyzing viewing habits and suggesting relevant content. Streaming platforms use machine learning to personalize experiences, increasing retention and customer satisfaction. AI also optimizes ad placement and content discovery, helping businesses grow their audience and maximize revenue.
Emerging Trends in Video Streaming for Business
Interactive Video
Interactive video is becoming a key trend for businesses looking to engage their audience. By allowing viewers to make choices or interact with the content, brands can create more personalized experiences, driving higher engagement and retention.
AI-Powered Personalization
AI-driven personalization is transforming video streaming by tailoring content recommendations based on user preferences and viewing history. This level of customization improves viewer satisfaction and helps businesses target their audience more effectively, boosting retention and monetization.
Hybrid OTT Strategies
Hybrid OTT strategies are gaining popularity as businesses look to combine both traditional TV broadcasts and streaming services. This model offers flexibility, allowing companies to reach broader audiences while benefiting from the scalability and cost-efficiency of streaming platforms like Dacast. This hybrid approach supports better engagement and enhances revenue potential.
How Businesses Leverage Video Streaming Technology for Growth
Several businesses are using video streaming technology to drive growth and engagement. For example, a leading online education platform has implemented low-latency streaming to offer interactive lessons to students across different time zones, improving engagement and course completion rates.
A fitness brand uses immersive video streaming to deliver live workout sessions to a global audience, helping them increase their subscription base. Additionally, entertainment companies are adopting video streaming for exclusive content delivery, utilizing flexible monetization models to generate steady revenue.
By leveraging AI-powered enhancements, secure content delivery, and global CDNs, these businesses are seeing significant benefits. Dacast’s white-label streaming solutions provide the tools needed for businesses to grow through reliable, secure, and monetizable video content.
Checklist for Businesses to Implement Video Streaming Successfully
To implement video streaming successfully, businesses should follow this checklist:
- Define your streaming goals—whether it’s engagement, training, or entertainment.
- Choose the right video streaming platform with white-label capabilities and global CDN delivery.
- Ensure your content is secure and protected with encryption and secure protocols.
- Invest in low-latency streaming to enhance user experience, especially for live content.
- Leverage AI-powered features for personalized content delivery and real-time video optimization.
- Implement effective monetization strategies, such as pay-per-view or subscription models.
- Test the user interface to ensure seamless navigation across devices and platforms.
- Plan for scalability to accommodate growing audiences without compromising performance.
By following these steps, businesses can harness video streaming technology to engage customers and generate revenue effectively.
Step-by-Step Guide on Setting Up a Live Streaming Workflow
Setting up a live streaming workflow in 2025 is straightforward with the right steps.
Start by choosing a reliable streaming platform like Dacast, which offers secure content delivery and monetization features.
Next, ensure you have the necessary hardware, including a good camera, microphone, and encoder to capture high-quality video and audio. For a smooth experience, select the appropriate streaming protocol, such as RTMP or WebRTC, depending on your needs.
Then, set up your streaming environment by connecting your equipment to the encoder and testing the video and audio settings. Configure your video player and integrate it with your platform to ensure seamless viewing for your audience. Make sure your CDN is in place for global content delivery and low-latency streaming.
Finally, promote your stream, monitor its performance, and engage with viewers during the event. This workflow ensures a smooth, high-quality live stream, optimized for both engagement and monetization.
Notable Video Streaming Equipment and Tools
There are several tools, including a variety of hardware and software, that brings all of this technology to life to make broadcasting easy for professionals without much technical know-how.
Let’s take a look at a few important tools for online video streaming.
Online Video Hosting Platform
One of the most important video streaming tools is an online video platform (OVP). This tool brings all of the other technology together and streamlines the broadcasting experience. A well-equipped OVP makes it possible for even brand-new broadcasters to get into the online video streaming game.
A video hosting platform does more than just host your videos, it provides you with a range of services and tools, such as:
- HTML5 video player
- Automatic transcoding
- Adaptive bitrate streaming
- Global video delivery
- Monetization and advertising
- Security and access control
Audio and Video Capture Equipment
Streaming equipment to capture your stream is non-negotiable. You need a reliable camera and audio-capturing tools to record your stream.
There are quite a few different cameras you can choose from for online video streaming, ranging from a simple webcam to a professional streaming camcorder. We recommend checking out our list of suggested live-streaming cameras to see some of the top options on the market.
As for audio and mobile capture equipment, sometimes the microphone that is built into the camera will do, but an external microphone is a quick fix that will take your audio quality to the next level. A simple handheld or lapel clip microphone is a small investment that can give your stream a more professional touch.
Having the right equipment makes it easier to produce high-quality live streams.
Encoding Hardware or Software
Encoding is another important part of the online streaming process. As we discussed before, encoding is what converts RAW videos to digital videos, which is important for streaming over the internet.
Broadcasters can choose from hardware and software encoders. In general, hardware encoders are much more expensive, but they are dedicated devices, which makes them a bit more powerful. Software encoders are much more affordable, and some are even free. Encoding software is almost as powerful as hardware encoders, and they can be updated like any other software.
Emerging Video Streaming Technology for 2025
Video streaming technology is still evolving at a rapid rate. New developments continue to push the boundaries of what is possible and improve different aspects of online streaming. For example, some emerging technologies is simply improving quality and experience while another new technology is exploring uncharted territories.
Here are a few examples of innovative streaming technology that you should keep an eye out for as they continue to develop and grow in popularity.
1. WebRTC
WebRTC is an emerging streaming project that was founded by Google to support real-time latency and peer-to-peer streaming.
WebRTC is currently used in a number of video conferencing apps, but online video platforms are slowly adapting to support this protocol to tap into its ultra-low latency capabilities. Although WebRTC is still a work in progress the future of the project will depend on how related live-streaming tools adapt to support it.
2. SRT
SRT is a developing streaming protocol that is known for low latency and reliable security. With those two characteristics and others, SRT is capable of streaming at a level that matches the combined forces of RTMP and HLS.
Another major benefit of SRT is that it is responsive. That means that it adjusts its carrying capacity based on the speed of the internet to avoid buffering, lagging, and failure.
At this time, very few online video platforms support SRT, but this protocol will likely continue to grow in popularity as more video streaming tools become accommodating.
3. Immersive Video Streaming
Immersive video streaming is another hot streaming technology that lies before us. This is a style of experiential streaming that helps viewers feel like they are in the video. There are a few types of immersive streaming including virtual reality and 360 video streaming.
360 video streaming uses a filming style that captures video from what would be the viewers’ point of view. This is relatively easy content to create, and it can be accessed on a regular video player. Simple cinematic elements can help to improve the user experience.
Virtual reality (VR) is a bit more advanced, and it requires a special headset for viewers to consume and experience. It also takes some more advanced work on the development side. In VR, viewers can move freely around the augmented reality.
Immersive streaming can be a great tool in both professional and casual settings. Immersive streaming has been used to enhance different areas of business, and it is also used for entertainment purposes.
This technology is still developing, so it will be interesting to see where it goes.
4. Ultra-High Definition Streaming
In recent years, high-definition 4K streaming was seen as an incredible feat. However, 5K and 6K streaming are on the horizon as cameras become more advanced and streaming infrastructure becomes more powerful.
Although cameras are capable of 5K and 6K streaming, the rest of the streaming technology is still catching up.
Deep Dive into Low-Latency and Interactive Streaming
LL-HLS (Low-Latency HLS)
Apple’s Low-Latency HLS (LL-HLS) is designed to reduce streaming delays while maintaining the reliability of traditional HLS. It achieves this by breaking video segments into smaller parts, allowing faster delivery to viewers. This technology is ideal for sports, live events, and interactive broadcasts where real-time engagement matters. Businesses using video streaming analytics can measure performance and optimize delivery for a seamless experience.
WebRTC and Interactive Live Streaming
WebRTC has become the go-to solution for ultra-low-latency streaming. Unlike traditional protocols, it enables real-time interactions without buffering, making it perfect for live auctions, gaming, and video conferencing. Businesses looking to boost engagement are leveraging WebRTC to create interactive experiences, improving audience participation and retention.
SRT Adoption and Future Growth
Secure Reliable Transport (SRT) is gaining traction for its ability to deliver high-quality, low-latency streams over unpredictable networks. As more platforms integrate SRT, businesses can ensure secure, uninterrupted content delivery while using video streaming analytics to refine their strategy.
Security and Compliance Considerations in 2025
AI-Based Threat Detection
AI is transforming video security by identifying threats in real time. Advanced algorithms detect piracy, unauthorized access, and cyberattacks before they cause harm. Businesses can use AI to monitor streaming patterns, flag suspicious activity, and prevent content leaks.
End-to-End Encryption for Secure Streaming
Protecting video content is critical, especially for businesses monetizing their streams. End-to-end encryption ensures that only authorized viewers can access premium content. Digital Rights Management (DRM) adds an extra layer of security by preventing unauthorized copying or distribution.
Zero Trust Security for Video Platforms
A zero-trust approach means never assuming a user or device is safe. Businesses should enforce strict access controls, requiring authentication at every step. Multi-factor authentication and role-based permissions help secure corporate video platforms from internal and external threats.
FAQs
1. What are the main challenges businesses face with video streaming?
Businesses often struggle with issues like video quality, slow load times, and unreliable content delivery. Ensuring a smooth streaming experience for a global audience can be tricky, especially when dealing with different devices and network speeds.
2. How can low-latency streaming improve my business?
Low-latency streaming reduces delay, making it ideal for live events and real-time engagement. It allows businesses to provide a seamless experience for viewers, which is crucial for industries like gaming, e-learning, and sports.
3. How does AI enhance video streaming for businesses?
AI helps optimize video quality, personalize content, and improve viewer engagement. It can also automate processes like captioning and content recommendations, making streaming more efficient and tailored to each viewer’s preferences.
4. How can I monetize my video streaming content effectively?
Businesses can monetize their streaming content through subscription models, pay-per-view, or ad-supported content. By using platforms with built-in monetization features, like Dacast, businesses can easily generate revenue from their content.
5. How can Dacast help with streaming challenges?
Dacast offers secure, white-label streaming solutions with global CDN delivery, ensuring high-quality, reliable video delivery. It also provides tools for monetization, analytics, and customer engagement, helping businesses grow and optimize their streaming strategy.
Conclusion
Online video streaming is very important to businesses and organizations that are looking to engage with their current audiences and extend their reach to new viewers.
Although some of the live streaming software technology we’ve mentioned in this post might sound complex or confusing, most broadcasters can get away with just knowing the basics. When you use a professional streaming solution, like Dacast, a lot of the “behind the scenes” technology is automatically configured. However, having a general idea of how it all works will help you make educated decisions throughout the process.
Looking for a powerful online video platform to help you start streaming? Dacast may be the option for you. Our platform is equipped with all of the tools that broadcasters need to host, manage, and deliver high-quality video content. Dacast offers white-label streaming, global content delivery, video monetization, top-notch security, and more.
You can try Dacast risk-free for 14 days by signing up for a free trial. Test all of our features and host a stream to see how our platform can work for you. Sign up today to get started. No contract, sign-up fees, or credit card required.
You can try Dacast and all its features free for 14 days, today.
For regular tips on live streaming, you’re welcome to join our LinkedIn group.
 Stream
Stream Connect
Connect Manage
Manage Measure
Measure Events
Events Business
Business Organizations
Organizations Entertainment and Media
Entertainment and Media API
API Tools
Tools Learning Center
Learning Center Support
Support Support Articles
Support Articles