10 Ways to Minimize Video Buffering Issues While Streaming
Video streaming has skyrocketed in popularity in various industries, especially post-COVID. Research shows that towards the end of 2023, almost 30% of internet users worldwide watched live streaming content weekly. However, in 2024, breaking news and sports were the most popular categories of livestream videos among U.S. audiences. With this surge in viewership, video buffering has become a major obstacle for live stream broadcasters
So how can you reduce video buffering and ensure a great customer experience as a broadcaster? Poor internet connection, not using a CDN, and live broadcasting software overload are just a few of the common culprits.
We are here to help if you’re in the media entertainment space or aiming to deliver a smooth e-learning experience. You’ll discover proven techniques to reduce video buffering, enhance your broadcasts, keep your audience engaged, and attract more viewers.
But first, let’s explore what video buffering is and what causes it.
Table of Contents
- What is Video Buffering?
- What Causes Video Buffering?
- Business Applications for Live Streaming
- 10 Ways to Stop Your Video From Buffering When Live Streaming
- AI and Automation-Based Solutions
- Measuring and Monitoring Buffering
- FAQs
- Time to Put an End to Your Video Buffering Issues
What is Video Buffering?
Video buffering occurs when your video hosting software preloads data segments into a reserved memory called a buffer. This allows your audience to watch video and audio content while more data downloads in the background, ensuring consistent playback.
Ideally, buffering is hardly noticeable if everything loads at the right speed. However, buffering often slows down, disrupting the streaming experience and frustrating your viewers.
When streaming, buffering may look like the spinning wheel or loading icon that temporarily halts playback.

Although buffering technically refers to the preloading process, it’s commonly associated with delays in playback, something broadcasters aim to avoid.
This post will focus on what causes buffering when streaming and how you can reduce it for a smoother, more engaging experience.
What Causes Video Buffering?
Video buffering can be caused by issues on either the user’s or broadcaster’s sides. While you can’t control everything on the user’s side, here are some potential causes to consider.
1. Internet Connectivity Problems
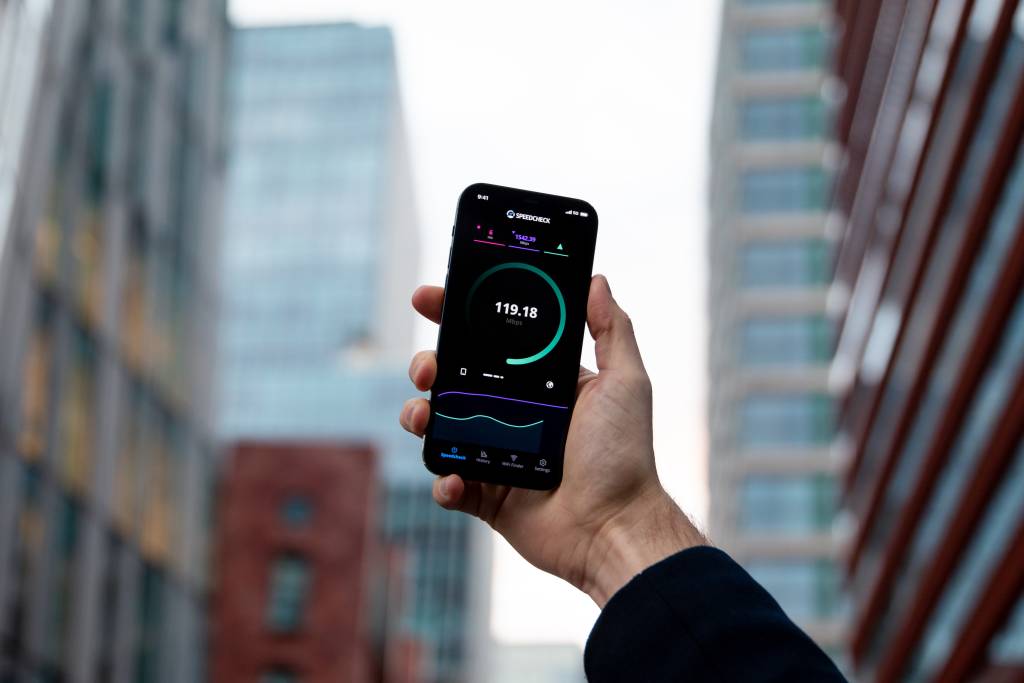

Your internet bandwidth needs to support HD video streaming. Every network has a bandwidth cap, determined by your internet service provider and connectivity plan. This is especially crucial for wireless connections.
If your bandwidth is too low to support the required data for streaming, buffering will occur. You’ll need to be aware of your internet speed before streaming video to allocate the buffer conveniently. Ensure your connection is fast enough for smooth playback. For example, if you’re streaming at 5Mbps, aim for at least 10Mbps for a consistent experience. Allocating 50% of your internet bandwidth to buffering usually prevents issues.
2. Heavy Video/Audio Files
Large video files, especially in high resolution, are more prone to buffering. A 4K video, for example, is much larger than a 720p video and can strain bandwidth. Users requesting higher-quality streams are more likely to experience buffering.
To prevent this, consider uploading multiple versions of your video files in various resolutions so users can stream the quality best suited to their device and internet speed. HD video streaming, while offering better quality, can also impact bandwidth due to the larger amount of data per frame.
3. Device Issues

Outdated devices may struggle with streaming, causing buffering. Even if your internet speed and file size are optimal, an older device may not meet the requirements for smooth playback. The browser used for streaming can also impact performance—some browsers handle streaming more efficiently than others, potentially causing buffering issues.
4. Issues with Your Streaming Provider
Your streaming provider could be experiencing issues that affect playback. These include:
- Network Overload: If your streaming provider is handling too many requests worldwide, the server may become strained, causing buffering across platforms
- Streaming Latency: This refers to the delay between a user request and the server’s response. Higher latency, often caused by server distance, can lead to buffering. Using a Content Delivery Network (CDN) can help reduce streaming latency and improve the experience.
- TCP Connection: The Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol are streaming protocols that ensure data packets reach the client in the correct order. A lost TCP connection can prevent the server from sending data, resulting in slow buffering.
Business Applications for Live Streaming
Businesses can strategically use buffering solutions to enhance the quality and reliability of their live streams. Here’s how various industries can benefit from optimized streaming and reduced buffering.
E-Learning and Webinars
E-learning platforms and webinars need to deliver smooth, uninterrupted streaming to keep audiences engaged. Multi-CDN switching ensures seamless playback for global audiences, reducing the risk of buffering while streaming. Additionally, AI-based transcription can provide real-time captions, minimizing the need for higher video resolution and reducing buffering delays
OTT and Media Companies
OTT platforms and media companies can use Server-Side Ad Insertion (SSAI) to minimize buffering caused by ad loads. This allows ads to be inserted server-side, ensuring a smoother playback experience. Multi-DRM encryption helps prevent unauthorized access, ensuring that video streaming remains uninterrupted, even when access is restricted.
Virtual Events and Conferences
Virtual events and conferences can benefit from real-time latency monitoring tools, which dynamically adjust server routing to reduce live streaming latency. This helps prevent buffering while streaming, ensuring smooth interactions for attendees and speakers.
E-Commerce and Product Demos
In e-commerce, shoppable video technology paired with low-latency streaming ensures customers won’t abandon their carts due to buffering delays. Optimizing the streaming experience, especially during live product demos, helps maintain customer interest and improves conversion rates.
10 Ways to Stop Your Video From Buffering When Live Streaming
Now that you understand the causes of video buffering, here are some strategies to fix them and provide a smooth streaming experience for your viewers.
1. Use Content Delivery Networks (CDN)

CDNs are essential to live video streaming as they ensure low latency and faster stream startup times by distributing content across multiple servers worldwide. Instead of requesting content from a single central server, users access it from the nearest server, reducing buffering and improving video quality.
For example, suppose you’re broadcasting from the US and a viewer in London accesses your stream. In that case, a CDN will deliver the content from a London-based server, reducing buffering caused by long-distance data transmission.
2. Consider VPS Hosting

A Virtual Private Server (VPS) allows you to host your network on a private server, giving you dedicated resources for a smoother streaming experience. With a VPS, your data isn’t shared with others, ensuring full performance and no video buffering when streaming. This is a great middle-ground option compared to shared hosting (which may slow down) or costly dedicated hosting.
The alternative to this would be shared hosting, which could get slow, or dedicated hosting, which is expensive. A virtual private server will suffice if you’re just starting out. Depending on your hosting service of choice, you can even scale your business on a VPS.
3. Embed Videos on Existing Streaming Platforms
If a CDN or VPS is out of your budget, consider embedding videos from established platforms like YouTube. These platforms automatically adjust video size and streaming quality based on a user’s internet speed, helping to reduce buffering issues. This is a cost-effective way to host your videos while benefitting from their built-in streaming optimizations.
This is especially convenient for businesses that want to use videos as part of their content marketing strategy. It’s easy to have such videos on your site because you’ll do very little of the encoding besides being free, as most of it is already done for you. For instance, YouTube auto-adjusts your video size depending on a user’s internet speed, which mitigates part of your video streaming buffering problems.
4. Choose the Right Web Hosting Service
Your video hosting platform plays a crucial role in preventing video buffering. Look for video streaming platforms that offer the following:
- Cloud Infrastructure: Platforms with cloud-based infrastructure (such as AWS or Google Cloud) are equipped to transcode, encode, and distribute content globally via CDN, ensuring smooth playback. The platform should also provide feasible ways to upload data from desktops, mobile devices, Dropbox, etc.
- Secure Video Hosting: Ensure your platform uses Digital Rights Management (DRM) encryption to protect your content from unauthorized access and interruptions.
- Customer Support: Opt for platforms with strong customer support, ideally with dedicated teams for your business needs. You’ll need better communication channels set in place and, if possible, a dedicated team to handle your specific business streaming needs.
- Plugins, Embedding, and Integrations: Choose platforms that can easily integrate with your website and social media, allowing you to embed videos seamlessly and reduce buffering issues. Your video broadcasting software should also enable you to embed videos on your websites and social media platforms.
5. Adaptive Bitrate (ABR) Streaming

Adaptive bitrate streaming (ABR) adjusts video quality for a smoother viewing experience and reduces video buffering. This technology detects and adjusts a user’s video quality settings based on their internet speed and available bandwidth.
How Adaptive Bitrate Streaming Works
When videos are uploaded, they’re not stored in one fixed bitrate. Instead, they are compressed into multiple bitrate streams, ranging from 50 to 4,000 kbps. If a user’s internet connection can’t support the highest bitrate (e.g., 4,000 kbps), the video will automatically switch to a lower bitrate, enabling smooth playback with minimal buffering.
While the video quality may fluctuate depending on the user’s bandwidth, adaptive bitrate streaming ensures continuous viewing by adjusting the stream in real time. It’s also important to note that ABR can automatically select appropriate bitrates based on the device’s screen size and resolution.
AI-Powered Adaptive Bitrate Streaming (AI-ABR)
Traditional ABR only adjusts video quality reactively, based on current network conditions. However, AI-powered ABR (AI-ABR) takes this a step further by predicting and optimizing bitrates in real time.
AI-ABR analyzes factors like network congestion, user device specifications, and even viewing habits to make proactive adjustments to the stream. This results in a more fluid viewing experience, with fewer quality dips and less buffering, especially during peak usage times or varying network conditions.
Using AI to optimize streaming, AI-ABR ensures that users receive the best possible experience, regardless of their connection or device. It will improve streaming quality while reducing video buffering.
6. Make Your Streaming Mobile Friendly
Mobile devices are now the primary way people access the internet, including streaming content. Ensuring your live streams are mobile-friendly is essential for reaching a wider audience and reducing video buffering.
Optimise Bandwidth for Mobile Streaming
Keeping your bandwidth below 1 Mbps helps minimise video buffering and ensures a smoother experience for mobile users. Many viewers stream over mobile networks, which can be inconsistent, so reducing bandwidth requirements prevents playback interruptions.
If your bandwidth is too high, mobile viewers are more likely to experience buffering issues. Before broadcasting, configure your encoder settings to offer lower bitrate options (e.g., 480p or adaptive streaming) to maintain smooth playback on mobile networks.
Ensure a Mobile-Responsive Streaming Platform
Your streaming platform and website should automatically adjust to different screen sizes and orientations. A mobile-responsive design ensures your content loads quickly, fits smaller screens, and remains easy to navigate.
For businesses, integrating low-latency streaming and adaptive bitrate streaming can further enhance mobile playback, reducing buffering while maintaining quality.
Making your live stream mobile-friendly will help you deliver a great customer experience and increase live viewership.
7. Avoid Overloading Your Encoder
An encoder transmits video from your camera, storage, or device to the internet. Your encoder handles major tasks, and overloading it can lead to buffering and disrupt your stream.
To prevent this:
- Avoid multitasking your encoder: Streaming while simultaneously recording high-resolution video can strain your system, leading to lag.
- Use a powerful encoder: Hardware encoders generally handle multiple tasks better than software-based encoders. If using a software encoder, ensure your computer has enough processing power to handle the workload.
Optimise encoding settings: Lowering your bitrate and using AI-powered encoding can help balance performance and video quality.
8. Have a High Upload Speed
Your upload speed is crucial in preventing video buffering during live streaming. If your preload speed drops below your playback speed, buffering occurs, causing delays and interruptions.
To avoid this:
- Your upload speed should be at least twice your bitrate. For example, if your stream is set to 5 Mbps, your internet upload speed should be at least 10 Mbps for stable playback.
- Use a wired connection instead of WiFi to reduce packet loss and network fluctuations.
- Optimise your network bandwidth by limiting other high-traffic activities (e.g., large file downloads) during streaming.
- Consider 5G or fibre-optic internet for more reliable and faster upload speeds.
If your bandwidth is low, upgrading your internet plan or using ABR can help maintain a smooth stream with minimal buffering.
9. Use Wired Over Wireless Connectivity

While Wi-Fi, 4G, and even 5G are convenient, they are more prone to network fluctuations, interference, and congestion, which can cause video buffering when streaming.
A smooth live stream is possible with the following:
- Use an Ethernet cable: This provides a consistent and uninterrupted connection, preventing bandwidth fluctuations.
- Minimise network congestion: If Wi-Fi is your only option, limit the number of devices connected to your network during streaming.
- Optimise router placement: Physical barriers, distance, and other wireless signals can impact Wi-Fi performance.
For the best results, a high-speed fibre connection with an Ethernet cable is the most reliable way to prevent buffering during live streaming.
10. Choose the Right Video Format
Using the correct video format can reduce video buffering and improve playback performance across devices.
The two best formats for buffer-free HD video streaming are:
- MP4: The most widely supported format with high-quality compression. It’s compatible with most devices and social media platforms like YouTube and Facebook.
- WebM: A more lightweight format optimised for HTML5 video streaming. It has smaller file sizes compared to MP4, making it ideal for low-bandwidth environments.
To reduce buffering issues, ensure your format supports adaptive bitrate streaming and uses an efficient video codec like H.265 (HEVC) for better compression and playback speed.
11. Cloud-Based Video Streaming & Edge Computing
Cloud-based streaming and edge computing significantly reduce video buffering by processing and storing content closer to the end user. Instead of relying on a centralised data centre, edge computing distributes caching and processing power to multiple edge servers worldwide.
Edge computing improves live streaming in the following ways:
- Lower Latency: Streaming data is processed at the nearest edge server, reducing the time it takes to reach the user.
- Reduced Network Congestion: By decentralising video delivery, bottlenecks and buffering issues are minimised, especially for HD video streaming and live events.
- Enhanced Scalability: Edge servers can handle high traffic spikes, ensuring stable playback during viral content moments.
In 2025, AI-driven caching further improves streaming and buffering performance.
- AI analyses user behaviour to predictively preload video segments before they are requested.
- Popular content is cached dynamically at edge locations, reducing buffering times.
- Real-time network adjustments ensure seamless playback even during bandwidth fluctuations.
12. Machine Learning for Predictive Buffering
Traditional buffering solutions react to slow connections, but machine learning (ML) now predicts buffering issues before they occur. AI-powered predictive buffering ensures that video segments are preloaded intelligently, minimising playback interruptions.
There are ways that AI can reduce buffering before it happens and here is how it’s done:
- User Behaviour Analysis: AI tracks individual watching habits and predicts when buffering is likely to occur.
- Adaptive Preloading: Based on a user’s previous activity, AI preloads video chunks to ensure smooth streaming.
- Dynamic Network Adjustments: Machine learning models detect network congestion and adjust bitrate and caching in real time.
For live streaming and on-demand video, AI-powered predictive buffering can:
- Reduce video buffering by up to 50%, improving user engagement.
- Optimise bandwidth usage, preventing unnecessary preloading.
- Enhance multi-device streaming, ensuring a smooth experience across mobile, desktop, and smart TVs.
13. WebRTC for Ultra-Low Latency Streaming
WebRTC (Web Real-Time Communication) is a game-changing technology for ultra-low latency streaming, enabling near-instantaneous data transmission between devices. WebRTC minimizes latency by establishing direct peer-to-peer connections unlike traditional streaming protocols that rely on buffering to stabilize playback. This is why it’s ideal for interactive applications such as live streaming, online gaming, video conferencing, and real-time auctions, where even a slight delay can disrupt the experience.
In 2025, WebRTC is being widely adopted by businesses looking to enhance real-time engagement. The protocol eliminates the need for intermediaries by using UDP (User Datagram Protocol) instead of TCP, ensuring faster data transmission. AI-powered network optimization techniques now enhance WebRTC by dynamically adjusting video quality based on changing network conditions, reducing packet loss, and maintaining smooth playback.
There is a growing demand for low-latency interactions in industries like telemedicine, education, and virtual events. It’s the reason WebRTC has become an essential tool for delivering seamless live video experiences without the buffering issues associated with traditional streaming technologies.
14. 5G & Private LTE Networks
5G networks continue to expand globally and businesses are increasingly using this technology for high-quality, low-latency video streaming. Unlike previous generations of mobile networks, 5G offers significantly higher data speeds, lower latency, and greater network reliability. It is what makes it ideal for live streaming, remote collaboration, and real-time broadcasting.
The ability to deliver HD and even 4K video streams with minimal buffering has made 5G an attractive solution. This is especially true for industries such as media, sports, and e-commerce, where smooth, uninterrupted streaming is critical.
Private LTE networks and dedicated 5G solutions are also gaining traction in 2025. Enterprises, event organizers, and media companies are deploying their own private 5G networks. It helps them to ensure a stable, high-performance connection without the congestion typically associated with public networks.
These private networks provide businesses with greater control over bandwidth allocation, security, and quality of service. With AI-driven network management, 5G and private LTE solutions can intelligently allocate bandwidth based on demand, preventing buffering.
15. Blockchain-Based Streaming Solutions
Decentralized streaming powered by blockchain technology is emerging as an innovative solution. It is intended to reduce network congestion and improve video delivery efficiency.
Unlike traditional streaming models that rely on centralized content delivery networks (CDNs), blockchain-based platforms distribute streaming data across multiple decentralized nodes, reducing the risk of bottlenecks and buffering. Using blockchain means video content is split into smaller data segments and delivered through a peer-to-peer network, ensuring faster and more reliable playback.
Some streaming services are now adopting blockchain-based models to enhance transparency, security, and cost efficiency. Smart contracts are being used to automate transactions between content creators and viewers. This helps to eliminate intermediaries and reducing operational costs.
AI-driven blockchain networks can also predict traffic patterns and allocate resources dynamically, optimizing streaming performance in real time.
AI and Automation-Based Solutions
AI is transforming video streaming by making content delivery faster and more reliable. Automation-driven solutions reduce buffering, improve quality, and optimize traffic in real time.
AI-Powered Content Delivery Networks (CDN+)
Traditional CDNs distribute content based on fixed routing, but AI-enhanced CDNs (CDN+) take it further. AI predicts traffic surges and dynamically redirects content to high-demand locations before congestion happens. It is used to reduce video buffering and ensure smooth streaming, even during peak usage.
Self-Healing Streaming Networks
AI-powered streaming networks can detect failures and instantly reroute traffic. If a server goes down or a network slows, AI identifies the issue and switches to the best alternative without disrupting the stream. Prevent buffering and keep video playback seamless.
Automated Buffering Detection & Fixing
Machine learning tools like QoE (Quality of Experience) Analytics analyze streaming performance in real time. They detect buffering patterns, pinpoint causes, and adjust content delivery before users experience interruptions. These systems continuously learn, improving playback quality over time.
Measuring and Monitoring Buffering
To deliver a seamless streaming experience, businesses must track and analyze buffering issues in real time. Advanced monitoring tools help identify problems before they affect viewers.
- Real-time Buffering Analytics: Platforms like Google Analytics, MUX, and Datadog provide real-time insights into buffering rates, playback interruptions, and network congestion. These tools allow businesses to pinpoint problem areas and optimize streaming performance instantly.
- Streaming Experience Score (SES): It is a key metric for assessing Quality of Experience (QoE). It evaluates factors like buffering frequency, video resolution, and latency to measure overall stream performance. A high SES indicates a smooth, high-quality viewing experience, while a low score signals areas that need improvement.
- Automated User Feedback Collection: AI-driven feedback systems gather viewer data, detecting when buffering issues arise. These tools adjust streaming parameters dynamically based on user responses, improving video delivery without manual intervention.
FAQs
What is video buffering?
Video buffering occurs when a stream pauses to load data before playback continues. It happens when the internet connection or streaming server cannot deliver data fast enough to keep up with the video. Buffering can be reduced by optimizing network bandwidth, using adaptive bitrate streaming, and leveraging Content Delivery Networks (CDNs).
What causes video buffering?
Video buffering is caused by slow internet speeds, network congestion, high-resolution video files, overloaded streaming servers, or outdated devices. Insufficient bandwidth, weak Wi-Fi signals, and inefficient streaming protocols can also contribute to buffering issues.
How do I fix a video buffer problem?
To fix video buffering, ensure you have a fast and stable internet connection, use a wired connection instead of Wi-Fi, reduce video quality, close background apps, and clear your browser cache. Using a Content Delivery Network (CDN) or adaptive bitrate streaming can also help optimize playback.
What is the difference between buffering and streaming?
Streaming is the continuous transmission of video or audio content over the internet, allowing users to watch in real-time without downloading the entire file. Buffering is the process of preloading a portion of the content to prevent interruptions, but if the data isn’t received quickly enough, buffering delays can occur.
Will increasing Internet speed stop buffering?
Increasing your internet speed can help reduce buffering, especially if your current speed is too low to support the video quality you’re streaming. However, other factors, such as server issues, high traffic, or the device you’re using, can also contribute to buffering.
Time to Put an End to Your Video Buffering Issues
Videos are central to modern content marketing, making video optimization essential for business success. Minimizing video buffering is a crucial part of enhancing the viewer experience, and this post has outlined the best techniques to tackle that challenge.
Investing in cutting-edge solutions like AI-driven Content Delivery Networks (CDNs), 5G connectivity, and WebRTC for ultra-low latency streaming. This way businesses can ensure a smoother and more reliable video experience for their audience.
Proactively measuring and addressing buffering issues through tools like real-time analytics and Quality of Experience (QoE) metrics is vital to maintaining a competitive edge.
Buffering isn’t just a technical problem. It’s a business challenge that can directly impact viewer engagement and brand perception. As an industry leader in video streaming solutions, Dacast provides the tools and expertise to help businesses overcome buffering, boost viewer satisfaction, and scale their streaming capabilities.
With Dacast, you can take advantage of advanced streaming technologies and seamless integration, all while elevating your live streaming strategy.
For exclusive offers, live streaming tips, and more, join our LinkedIn group. If you have specific questions, our team is here to help. Don’t hesitate to reach out!
 Stream
Stream Connect
Connect Manage
Manage Measure
Measure Events
Events Business
Business Organizations
Organizations Entertainment and Media
Entertainment and Media API
API Tools
Tools Learning Center
Learning Center Support
Support Support Articles
Support Articles